pdf The use of geodiversity information in biodiversity assessments Popular
2462 downloads
Helena Tukiainen
Geography Research Unit, Universtiy of Oulu
Maliniemi, Tuija, Ecology and Genetics Research Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Nissinen, Elina, Geography Research Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
Kapfer, Jutta, Norwegian Institute of Bioeconomy Research (NIBIO), Tromsø, Norway
Hjort, Jan, Geography Research Unit, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
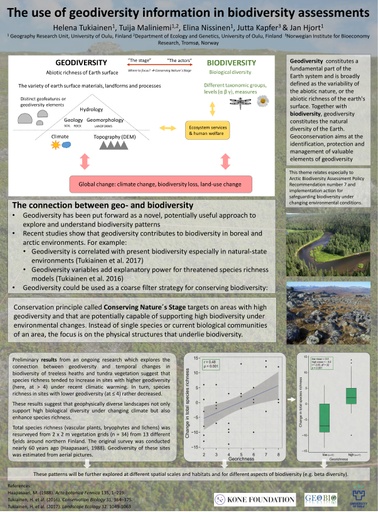
 In recent years, geodiversity has been put forward as a novel, potentially useful approach to explore and understand biodiversity patterns. Geodiversity is commonly defined as the variety of earth surface materials, landforms and processes (geological, hydrological and geomorphological), or the abiotic richness of Earth surface. Recent studies have shown that geodiversity is related to landscape-scale species richness in northern environments. However, conserving current biodiversity based only on present communities may not guarantee diversity in the future. Better option might be to conserve the abiotic environment on which the biological diversity is based on. This conservation principle, called Conserving Nature´s Stage, targets on areas with high geodiversity and that are thus capable of supporting high biodiversity under future environmental changes. This would be one possibility when considering Arctic Biodiversity Assessment Policy Recommendation number 7 and implementation action for safeguarding biodiversity under changing environmental conditions. Here we summarize the existing knowledge on the relationship between geo- and biodiversity and study how diverse physical environments are related to temporal changes in plant species richness in subarctic tundra under recent climatic warming.
In recent years, geodiversity has been put forward as a novel, potentially useful approach to explore and understand biodiversity patterns. Geodiversity is commonly defined as the variety of earth surface materials, landforms and processes (geological, hydrological and geomorphological), or the abiotic richness of Earth surface. Recent studies have shown that geodiversity is related to landscape-scale species richness in northern environments. However, conserving current biodiversity based only on present communities may not guarantee diversity in the future. Better option might be to conserve the abiotic environment on which the biological diversity is based on. This conservation principle, called Conserving Nature´s Stage, targets on areas with high geodiversity and that are thus capable of supporting high biodiversity under future environmental changes. This would be one possibility when considering Arctic Biodiversity Assessment Policy Recommendation number 7 and implementation action for safeguarding biodiversity under changing environmental conditions. Here we summarize the existing knowledge on the relationship between geo- and biodiversity and study how diverse physical environments are related to temporal changes in plant species richness in subarctic tundra under recent climatic warming.

